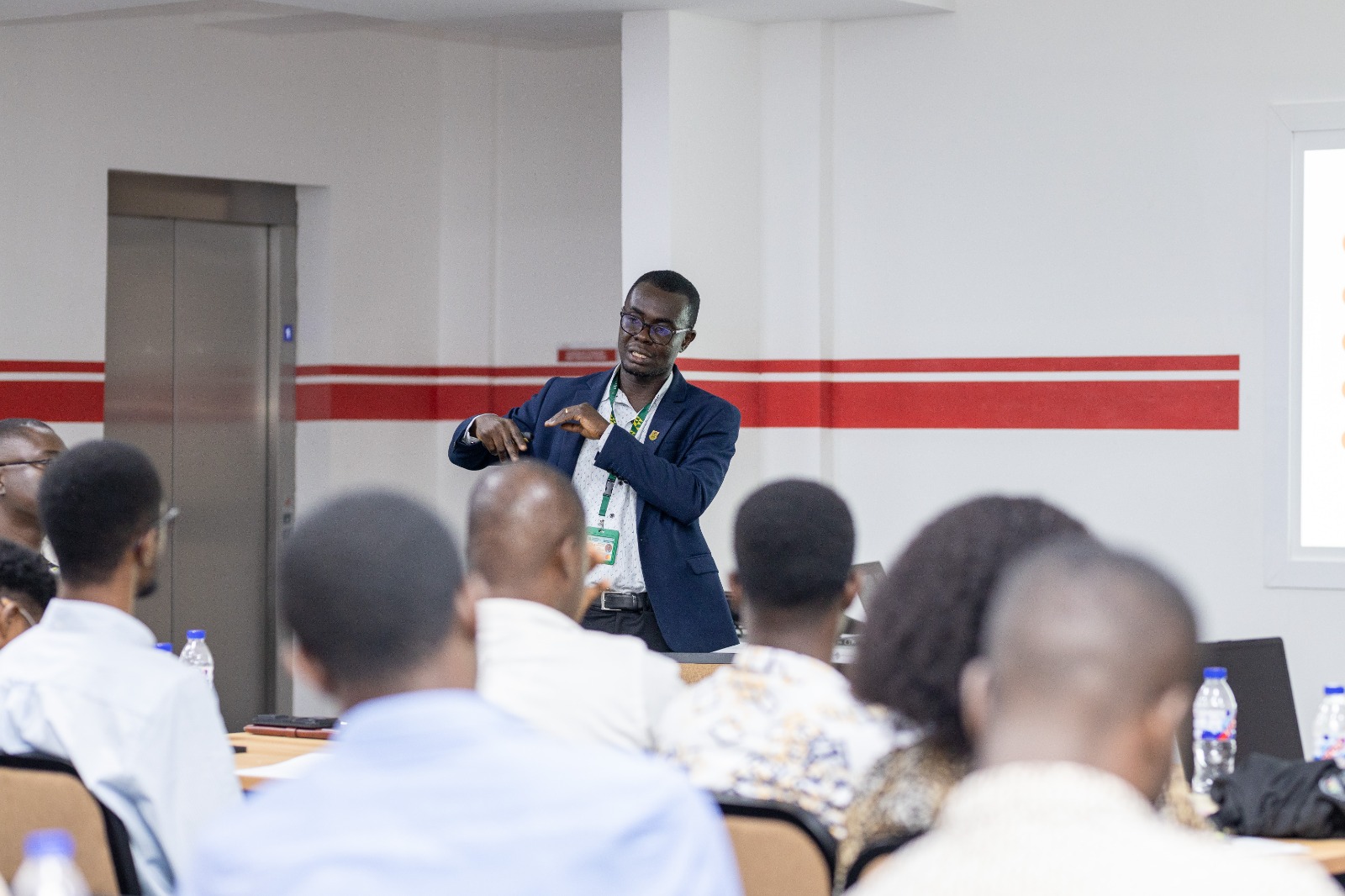
The KNUST E-Learning Centre has announced a new strategy aimed at redefining its role in digital education and positioning itself as a leader in educational technology on the continent.
The strategy was outlined this week by the Director of the Centre, Prof. Emmanuel Kofi Akowuah, who said the unit will prioritise innovation, financial independence and high-impact digital learning over traditional support services.
Prof. Akowuah said the shift aligns with the university’s broader ambition to move “from Excellence to Eminence.”
“We want to establish the KNUST E-Learning Centre as a globally recognised leader in innovative, sustainable and high-impact digital education,” he said.
He noted that the Centre must be known for transforming learning rather than for content production or livestreaming. The vision is anchored on three principles for all future projects: Innovation, Income Generation and Impact.
Prof. Akowuah said performance expectations will be heightened as the Centre adopts the new direction.
“Good enough will not be acceptable. We are going to hold ourselves to a higher standard,” he stated.
He added that the Centre will seek financial self-reliance, encouraging staff to develop monetisable projects to reduce dependence on the university’s central budget.
The Director also stressed the need to expand the Centre’s footprint across the African digital learning sector and dispel the perception that its work is limited to technical support. The strategic goal, he said, is for the Centre to become the authority on electronic learning policy and practice within the university ecosystem and beyond.
“We are shaping the future of global education right here at KNUST,” he said, underscoring the Centre’s ambition to lead technological change across the region.
The Centre is now transitioning into an execution phase focused on projects that demonstrate high impact and visibility. The 2026 work plan prioritises innovation in three areas:
- Digital Assessment – developing technology, potentially supported by Artificial Intelligence, to efficiently process and grade handwritten examinations.
- Immersive Learning – deploying Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) solutions for practical training, including safety-critical and hazardous environments.
- Student Engagement – engineering new tools to increase student interaction with digital learning materials amid low usage of traditional Learning Management Systems (LMS).
Prof. Akowuah said future projects will receive resources only if they align with the revised strategic vision.